“Can you go beyond high performance?” That’s a penetrating question Jason Jaggard, founder and CEO of the executive coaching firm Novus Global, asks in his powerful and popular article that bears that title. My good friend and StrengthsFinder coach, Dan Leffelaar, who is COO and partner at Novus Global, had exposed me to the company after he joined. Later he would introduce me to one of their very competent coaches, Joseph Thompson. It was Joseph who then drew my attention to this article even before we would have our first formal coaching session. By the way, I’ve said it before and it’s worth repeating, never hire a coach who doesn’t have a coach!
DIFFERENTIATION–OR WHATEVER YOU CALL IT
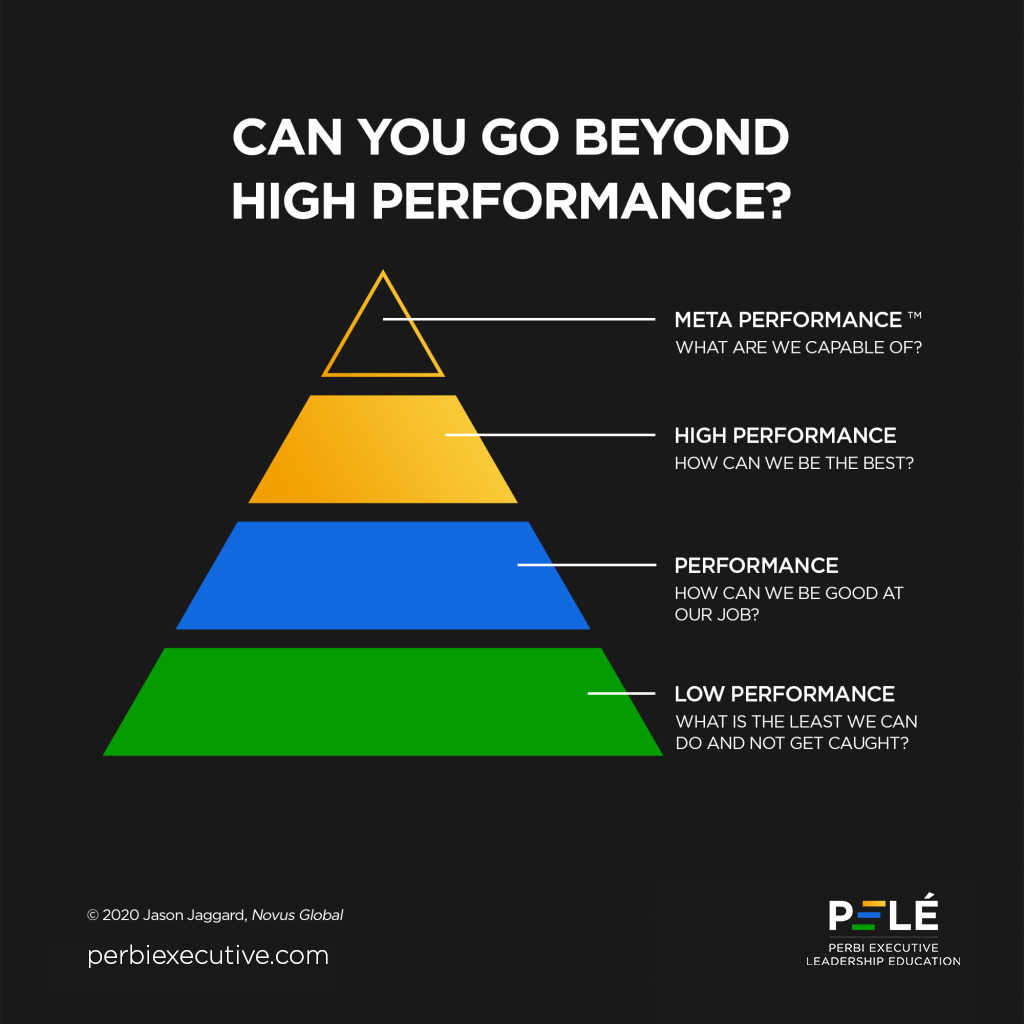
It is not uncommon for managers to categorize workers in the marketplace into three: low performers, performers and high performers. Over a decade ago, I remember reading about this idea from long time General Electric CEO Jack Welch’s book Winning. He called it differentiation, separating the sheep from the goats. According to Jack, differentiation is a process that requires managers to assess their employees and separate them into three categories in terms of top performance: top 20 percent, middle 70, and bottom 10. Then—and this is key—it requires managers to act on that distinction.
 This three-level categorization is common in management practice
This three-level categorization is common in management practice
Whatever different percentages one uses to divide the three levels (and some just use the Pareto principle to divide the top 20% from the remaining 80%), the questions the people in each band ask themselves that result in their kind of performance are intriguing:
- Low Performers–“What is the least we can do to get by–and not get caught?”
- Performers–“How can we be good at our job?”
- High Performers–“How can we be the best?”
Often the morale of the story is “be the best,” be a high performer. Or, in the precious words of my dad’s alma mater (in Latin), Vel primus vel cum primis. To wit: either the first or with the first. But that is precisely the problem. High performers typically stop growing because they feel (or are made to feel) they are the best, or among the best, and have hit their peak when that is far from the truth! That’s the challenge of comparing ourselves to others instead of to our own potential. Don’t forget the saying that “in the land of the blind, the one-eyed man is king.” What is high performance about one eye just because everyone else you’re compared with is blind?
In fact, not only does Jason point out two common mistakes of high performers here but Novus Global as a practice firmly believes “attracting and retaining high-performers is a mistake and doing so creates a predictable set of problems.” You probably have met a lot of high performers who are still unhappy. Barring greed and envy, could Abraham Maslow’s observation be the cause? “If you plan on being anything less than you are capable of being, you will probably be unhappy all the days of your life.”
META-PERFORMANCE
So “can one go beyond high performance?” remains the question. “What comes after high performance?” I’m glad you asked. “If your team doesn’t have a clear and compelling answer to the question “What comes after high performance?” then you absolutely have an unnecessary cap on the possibilities of your leadership and the impact of your organization,” says Jason. The answer lies in a word he’s coined: meta-performance. And this is “meta” is not like “meta-data” but “meta” as in “metamorphosis,” like a caterpillar transforming into a butterfly. A meta-performer isn’t committed to being the best (“how dull,” Jason says)… a meta-performer is committed to constantly exploring capabilities.
 An introduction to Meta-Performance
An introduction to Meta-Performance
Unlike “What is the least we can do to get by–and not get caught?” (Low Performers), “How can we be good at our job?” (Performers) or “How can we be the best?” (High Performers), Meta-Performers ask themselves, “What are we capable of?” That is a potent question in and of itself, but to process that with a competent and caring coach is even more powerful!
I often say to people, I may not have been the best of medical students (I was a low performer) but I was a very good doctor (high performer). But as good a doctor as I was, the question of what I was capable of sent me on a totally different trajectory from my peers, from authoring books and motivational speaking through military experience and peacekeeping with the United Nations, to pastoring, restarting life as a Canadian immigrant and becoming CEO of a number of non-medicine related ventures, some with a budget of a few million dollars.
Meta-performance is akin to what my mentor John C. Maxwell calls The Law of the Rubber Band: Growth Stops When You Lose the Tension Between Where You are and Where You Could Be. The meta-performance life happens somewhere between feeling ‘just right,’ taut enough to be best at tying things up, to tearing up because we fail to embrace our God-given limits. Often times, we are poor judgers of thse book ends, and having a discerning coach to assist on this journey is vital.
“IMPOSSIBLE” ACCORDING TO WHO?
In what area(s) of your life have you lost your stretch and settled? Create some specific means for stretching in these areas of your life. Go back to your 2021 goals and ensure they’re not only S.M.A.R.T. but that they also STRETCH. Remember, “Only a mediocre person is always at his best,” saysW. Somerset Maugham, putting things in a way that hits home, hard. “Ouch,” says the best performers.
Walt Disney used to say, “It’s kind of fun to do the impossible.” I know the feeling, a little bit. Nelson Mandela was right: “It always seems impossible until it’s done.” I find it not only a powerful meta-performance question to ask “What am I capable of?” but also in line with that to inquire, “What sort of person must I become to be capable of that?” Then with Almighty God’s help, “just do it,” do the “impossible.”











